Lenalidomide: what it is and what you need to know
Lenalidomide (brand name Revlimid) is an oral cancer drug doctors use mostly for multiple myeloma, certain myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and some lymphomas. It helps the immune system fight cancer and can slow tumor growth. If your doctor prescribes it, you’ll likely be on a strict plan with regular blood tests and clear safety rules.
What lenalidomide treats and how it works
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory agent. In simple terms, it boosts parts of your immune system and blocks signals that cancer cells use to grow. Common uses include maintenance therapy after myeloma treatment, treatment for relapsed myeloma, and MDS with certain genetic changes. Your doctor will explain why it’s chosen over other options based on your diagnosis and test results.
How quickly it works varies. Some people notice fewer symptoms within weeks, while others need months to see stable blood counts or tumor markers. Expect your care team to measure progress with lab tests and scans rather than how you feel day-to-day.
Safety, monitoring, and smart tips
Lenalidomide has real risks you must take seriously. The big ones are low blood counts (low white cells and platelets), blood clots, and a high risk of birth defects. Because of that last risk, lenalidomide is only given under strict pregnancy-prevention rules—both men and women of childbearing potential must follow testing and contraception requirements. If you’re pregnant or planning pregnancy, do not take it.
Your care team will check your blood regularly—usually weekly at first, then less often if stable. Call your doctor for fever, unexplained bruising, heavy bleeding, sudden shortness of breath, or calf/leg pain. These can be signs of infection, low platelets, or a blood clot and need fast attention.
Lenalidomide is cleared by the kidneys, so dose changes are common if you have kidney problems. It doesn’t rely on liver enzymes like many drugs, but always tell your doctor about supplements and medications—especially blood thinners—so they can manage clot risk and interactions.
Cost can be high even for generic versions. Check with your insurance, ask about manufacturer or charity assistance programs, and talk to the clinic’s financial counselor. If you’re tempted to shop online, only use verified pharmacies and never skip the prescription or safety screenings. Shady sources can sell counterfeit or unsafe meds.
Final everyday tips: keep a list of your meds, bring questions to clinic visits, keep infection precautions (hand-washing, avoiding sick people) while your white counts are low, and use reliable contraception if you or your partner could become pregnant. Talk openly with your team—the right monitoring and small lifestyle steps make lenalidomide safer and more effective for most patients.
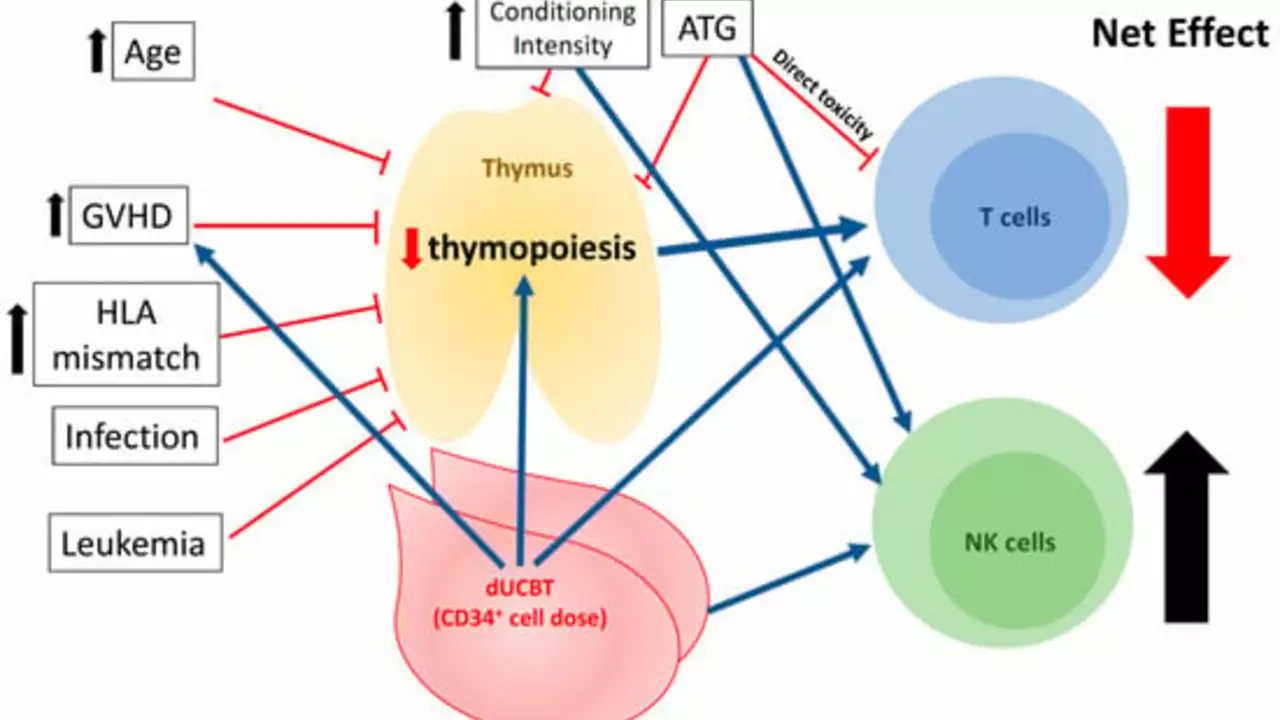
After delving into the topic, I've learned that lenalidomide is increasingly being utilized in the management of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). This is a common complication following a bone marrow or stem cell transplant, where the donor cells start to attack the patient's body. Lenalidomide has shown promising results in mitigating this reaction, helping to improve patient outcomes. There's definitely more research needed here, but the initial results are encouraging. So, in the future, we may see lenalidomide becoming a standard part of GVHD treatment.
Continue Reading