Medication Dosing: How Proper Doses Prevent Harm and Maximize Effectiveness
When you take a pill, the medication dosing, the precise amount of a drug given at a specific time to achieve the desired effect without causing harm. Also known as drug dosage, it’s not just about following the label—it’s about matching your body’s needs to the drug’s behavior in your system. Too little and it won’t work. Too much and you risk toxicity, organ damage, or even death. This isn’t theoretical. People with kidney disease, older adults, and children often get dosed wrong because standard recommendations don’t account for how their bodies process drugs.
Pharmacokinetics, how your body absorbs, moves, breaks down, and gets rid of a drug. Also known as drug metabolism, it’s the science behind why a 50mg dose works for one person but makes another sick. For example, renal dosing, adjusting medication amounts based on kidney function, is critical for drugs like Lasix or NSAIDs. If your kidneys can’t clear the drug, it builds up. That’s why people with chronic kidney disease need lower doses—or different drugs entirely. Then there’s drug interactions, when one medication changes how another works in your body. Also known as medication interactions, they can turn a safe dose into a dangerous one. Levothyroxine doesn’t absorb well if you take it with a proton pump inhibitor. Warfarin can cause bleeding if mixed with certain antibiotics. These aren’t rare edge cases—they happen every day in clinics and homes.
Medication dosing isn’t just a number on a bottle. It’s shaped by your age, weight, liver and kidney health, other meds you take, and even what you eat. A standard dose for a healthy 40-year-old might be deadly for an 80-year-old with diabetes and high blood pressure. That’s why some drugs—like antidepressants or statins—come with warnings about side effects that only show up when doses aren’t personalized. And when you buy meds online or switch generics, you’re not just changing the brand—you might be changing how your body handles the drug.
Below, you’ll find real stories and science-backed guides on what happens when dosing goes wrong—and how to make sure it doesn’t happen to you. From how prednisone messes with your mood at high doses, to why melatonin’s effect changes with age, to how kidney disease turns common painkillers into toxins—these posts don’t just warn you. They show you how to stay safe, ask the right questions, and take control of your treatment.
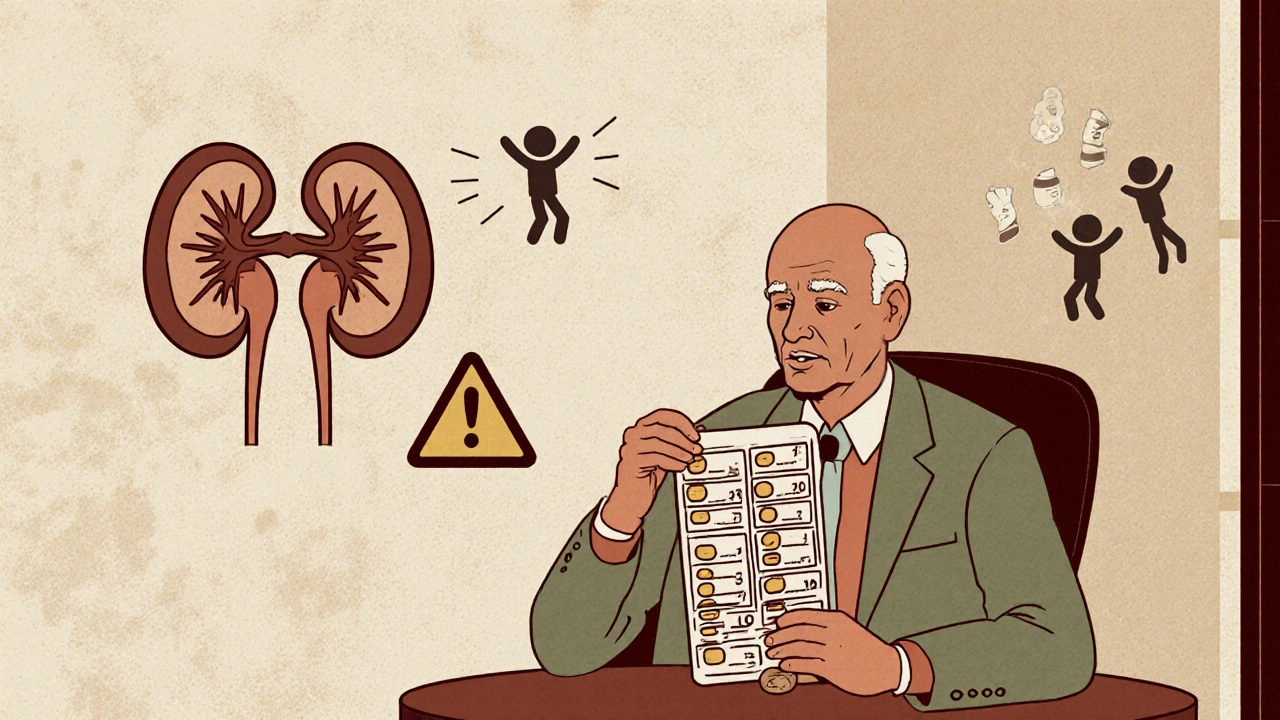

Elderly patients with kidney impairment are at high risk of drug toxicity. Learn how to adjust medication doses using GFR, avoid dangerous errors, and use the latest guidelines to keep seniors safe.
Continue Reading